
[Design] HCI 2024: Usage of Voice Assistant based on Context & Space
Feb 09, 2024 | SEOUL
DRIMAES product mentioned within this articles are offered by DRIMAES, Inc.
Voice assistants, a technology that employs artificial intelligence to process voice commands and deliver responses, have become an integral part of our daily lives. These assistants are now widely used across various devices and platforms, making everyday tasks more convenient. Moreover, their application in the mobility sector, especially within vehicle environments, is revolutionizing user experience (UX), becoming a key innovation driver. With numerous automakers accelerating the integration of voice recognition and GPT-based features, DRIMAES' collaboration with Seoul Women's University at the HCI (Human-Computer Interaction) 2024 conference offers insightful analysis and utilization of voice agents from the perspective of Context & Space.
Context & Space #1: Smart Homes and Voice Assistants

In smart homes, voice assistants enable bidirectional communication between all home elements and the owner, optimizing routines tailored to the owner's lifestyle. The typical smart home setup allows users to remotely control and manage home devices like lights, refrigerators, thermostats, gas valves, and TVs through various devices, such as smartphones and tablets. This setup supports multiple actions, including touch and voice, and integrates smart speakers and smartphones to provide information through voice interfaces and visual elements, enhancing intuitive recognition.
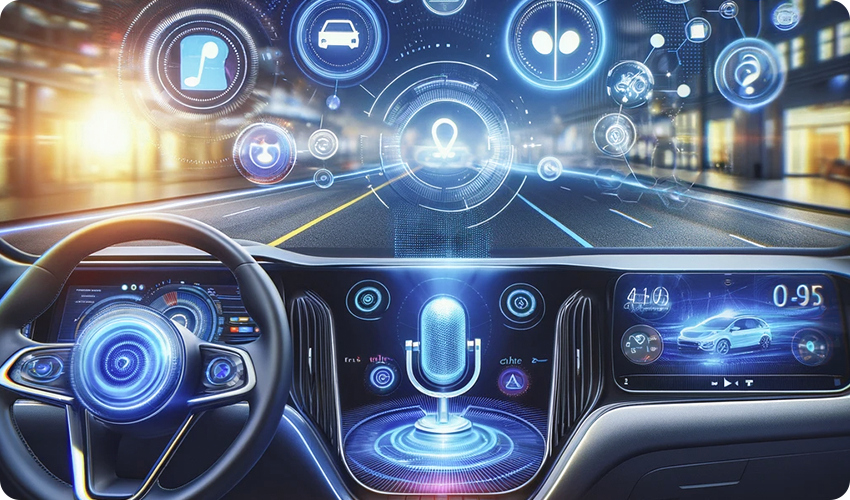
Context & Space #2: Vehicle Spaces and Voice Assistants

Context & Space #3: Between Vehicle Spaces and Smart Homes

The utilization of voice assistants in both vehicle and smart home environments provides significant convenience to users, sharing many similarities in their application. For instance, both environments adopt voice recognition for communication, allowing hands-free user interaction and using visual elements like ambient lighting to enhance context-aware interactions. The visual design of voice assistants in both settings also shares similar layouts and styles, offering a familiar and consistent user experience.
However, there are distinct differences in how voice assistants are utilized in these environments. In smart homes, voice assistants are designed for user convenience, primarily controlling appliances and requesting information. These interactions are mostly optional, focusing on enhancing the user's lifestyle. In contrast, in-vehicle voice assistants emphasize vehicle maintenance and safety, proactively offering suggestions related to vehicle upkeep and safety based on sensor data and detecting changes in the vehicle's condition, often making this information provision essential due to its direct impact on user safety.
Context & Space #4: Optimization Strategies
Research in vehicle spaces shows that drivers frequently check visual information to determine if voice assistant tasks have been completed, while in smart homes, dependency on voice assistants varies by usage scenario, affecting the use of visual information. How can voice assistants be optimized within the constrained environment of a vehicle?
Key considerations for designing voice-based UX in vehicles include:
1. Intuitiveness and Simplicity:
Visual information in vehicles must be intuitive and straightforward to avoid distracting the driver and impacting safety. Important information should be emphasized with minimal visual elements.
2. Context Awareness and Adaptability:
In-vehicle voice agents must recognize driving conditions and user behavior patterns, providing appropriate visual information accordingly.
3. Safety-Centric Design:
All visual information must prioritize driver safety, ensuring efficient information delivery without diverting the driver's focus from the road.
4. Personalization and Learning Capability:
Customizing visual information and interaction methods based on user preferences and driving styles is crucial, with voice agents learning user patterns to offer tailored information, enhancing the user experience.
DRIMAES focused on designing the utilization of visual information during command processing. Instead of concentrating user attention on waiting for command execution, the design emphasizes driving by assisting with audio-visual content to effectively deliver voice assistant feedback.
1. Auditory Feedback:
- Voice updates from the voice agent about the "status of processing."
- Notification sounds to indicate the processing status.
2. Visual Feedback:
- Micro-interactions that show the progress of processing, indicating the stages of the task.
- Use of supplementary displays such as Head-Up Displays (HUD) to provide visual guidance and direct information.

DRIMAES’ research, presented in collaboration with Seoul Women's University at the HCI 2024 conference, signifies a major advancement in exploring the future of interaction between machine learning and AI technologies in mobility. The derived principles of intuitiveness, context awareness, safety-centric design, and personalization lay the foundation for innovative applications of in-vehicle voice assistants, promising to maximize driver experience and revolutionize driving environments.
The future of in-vehicle voice assistants extends beyond executing commands to providing customized information and services based on the driver's behavior, preferences, and situations. Advances in AI, GPT, and machine learning will enable voice agents to more accurately predict drivers' intentions and needs, adapting in real-time. Enhanced visual and auditory feedback systems will ensure drivers can access necessary information safely and easily, even in complex situations.
The evolution of in-vehicle voice assistants aims not just at technological advancement but at redefining interactions between drivers and vehicles through user-centered design and personalized experiences. This approach enriches the mobility experience, transforming vehicles from mere transportation means into integrated lifestyle partners. The development of in-vehicle voice assistants will not only innovate user experiences in future mobility environments but also introduce a new paradigm in how we interact with vehicles.

